You can create an action that queries the Autotask API and can be used to retrieve an object such as a Ticket. The results of the query can then be stored in a variable for use at a later point in your rule.
Auto-expand linked objects
When retrieving an object from Autotask, many of the object's properties will contain an integer value that represents a related object or picklist. Often you will want to know the display value for this property (e.g. on a Ticket entity, the value Complete rather than 5 ). However, in the past it was cumbersome to find the display value as this meant also querying the Autotask API for the related object (in order to retrieve its properties).
MSPintegrations eases this process by automatically retrieving related objects, meaning there is no need to query multiple times.
When you query for an Autotask object you will therefore have access to the the object's properties, as well as the properties of any objects related to the retrieved object. This makes it simple to query something like "is the resource who completed the task still active?"
What are Autotask Entities?
Database objects stored in Autotask are represented by entities, each having its own ID. Entities also have properties (data fields) that describe the entity. For example, an Account entity will have an ID and various properties such as AccountType .
There are over 150 entity types in Autotask, with corresponding properties. The full list of entities can be found in the Autotask API documentation.
What is returned from the query?
The query returns the object you requested and any linked entities. The properties of all the entities will be returned as well.
For example, if you query for an Account then you will also receive any linked entities, for example the Resource entity that represents the Account Manager . For the Account itself you will have all the properties such as AccountName and for the Resource you will have properties such as Email. This is outlined below:
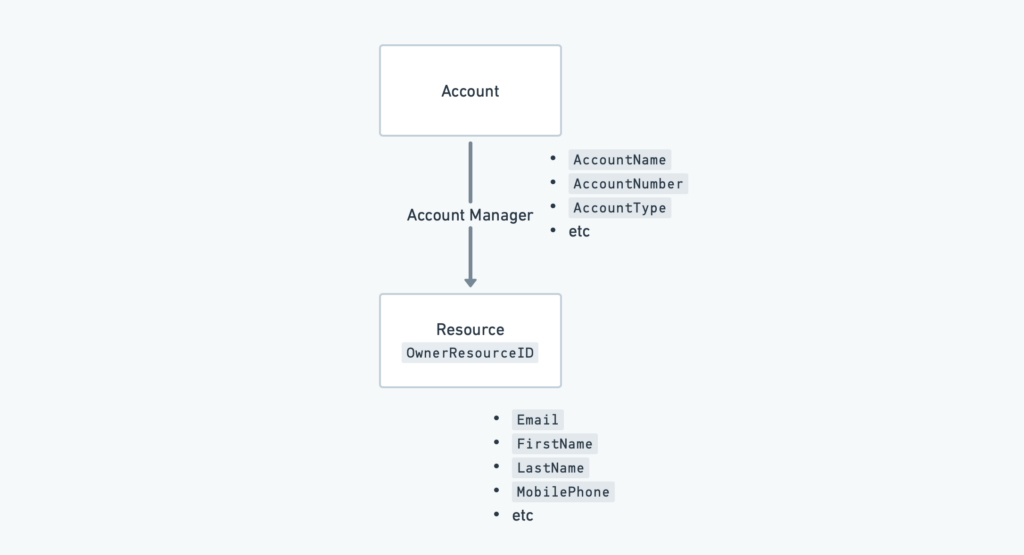
The linked entities returned will depend on the object you have queried. In general anything represented in Autotask with an ID can be considered an entity. In Autotask you should be able to see some entities linked within the UI (e.g. the Primary Contact linked on the Account entity). The full list of entities and their properties can be found in the Autotask API documentation.
How to query for an object
- Select
API: Query for one objectin thePerform this actiondropdown. - Select the
Entity Typefrom theAutotask Entity Type to Querydropdown, e.g.Ticket. - Use the
Query Parametersection to define the query that will be run against Autotask.- You can choose to either have an object return only if all statements match
All of these (SQL comparison 'and')or if any statement matchesAny of these (SQL comparison 'or'). - By default there is 1 group of conditional statements. You can use the add new conditional statement button to add another parameter to the query. You can also new groups of statements in order to use both
ANDandORqueries.
- You can choose to either have an object return only if all statements match
- On the left in
Store the results in variableyou can name the variable where the query results will be stored e.g.custom.ticket. - In future steps this variable can be accessed using e.g.
{{custom.ticket.and the properties and linked objects will appear in the autocomplete menu.
How do I use the query results?
If you store the query results in a custom variable, you can access the entities using the autocomplete menu.
For example:
- Store the
Accountentity in acustom.accountvariable - In another action, access the account name through
{{custom.account.AccountName}} - Access the account manager's email address through
{{custom.account.OwnerResourceID.Email}}
Sorting the query results
If your query returns more than a single result, only the first result will be returned to MSPIntegrations. You can optionally sort the results in order to make sure the first object returned is the one you want.
Using a custom variable as a condition in your rule
You can use custom variables within a condition so that an action is only performed in certain circumstances. You can define this in Only perform this action if the following condition is met .
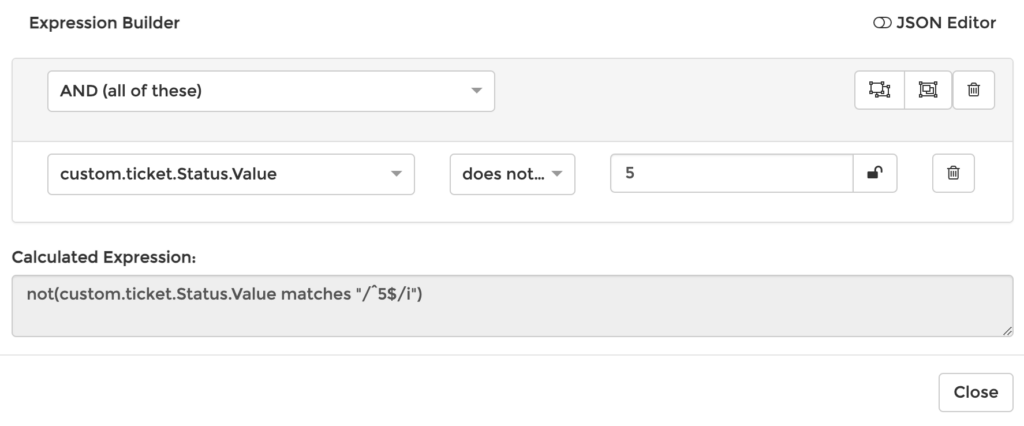
For example, if you don't want a ticket to be updated if it is already complete:
- Query Autotask for the
Ticket - Store the result in a variable e.g.
custom.ticket - In the next step check that the ticket's status
custom.ticket.Status.Valuedoes not equal5(which represents 'Complete') - Tickets processed using this action will only be updated if they are are still open
References
- You can read more about the variables available for an incoming email in the documentation.
- The properties available for Autotask entities are outlined in the Autotask documentation.
Legacy Behavior
Prior to mid-2023 it was not possible to access the linked objects in MSPintegrations. Instead you had to have multiple query steps using IDs that were retrieved in a previous step. If you choose, you can now update your rules to consolidate the steps.
As a result of the update some values in the API will have changed name. For example the legacy syntax {{custom.account.CreatedByResourceID}} and current syntax {{custom.account.CreatedByResourceID.id}} represent the same value. The update is backwards-compatible so there is no need to change existing action steps.
